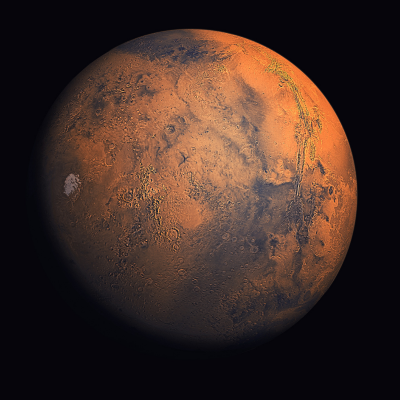
The Solar system
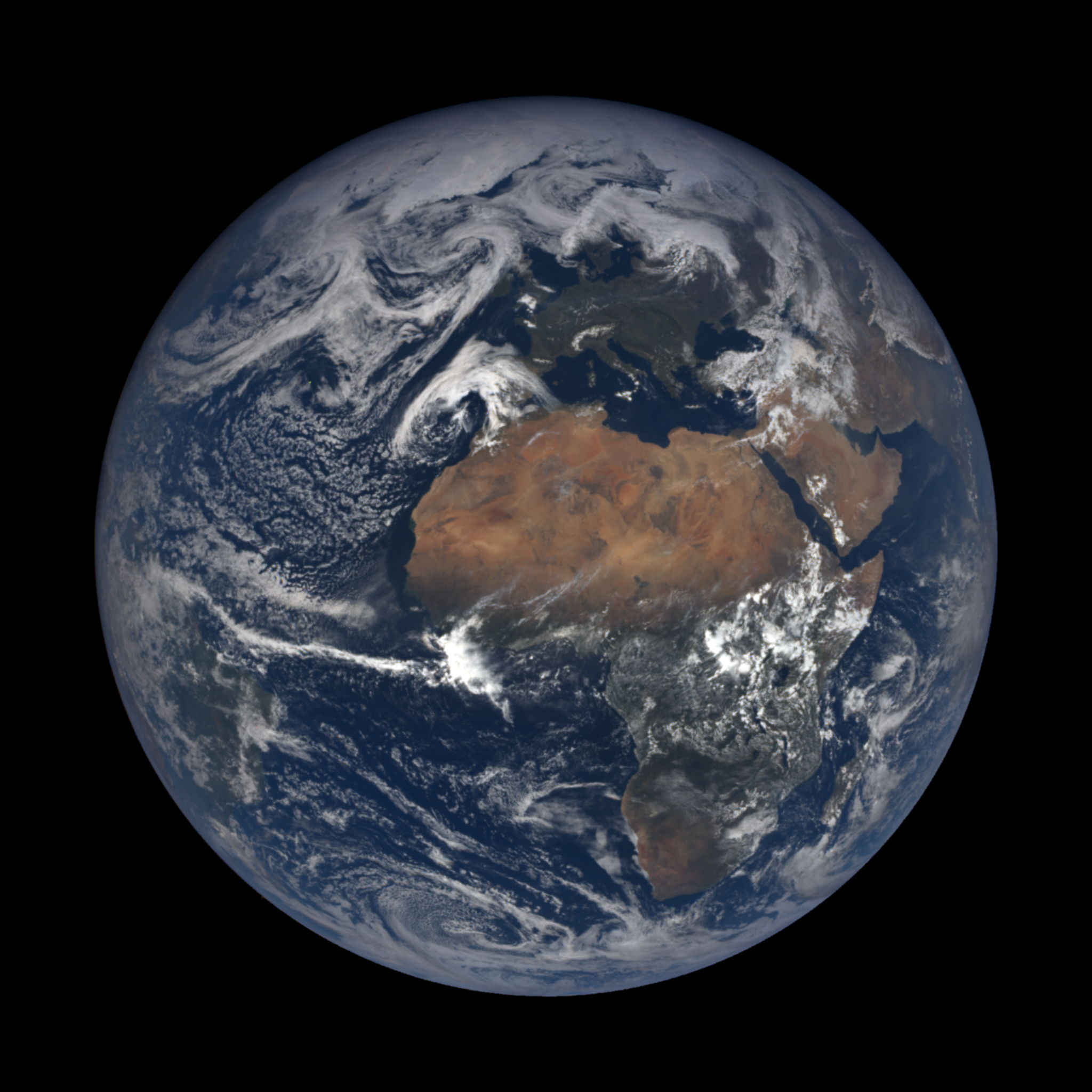
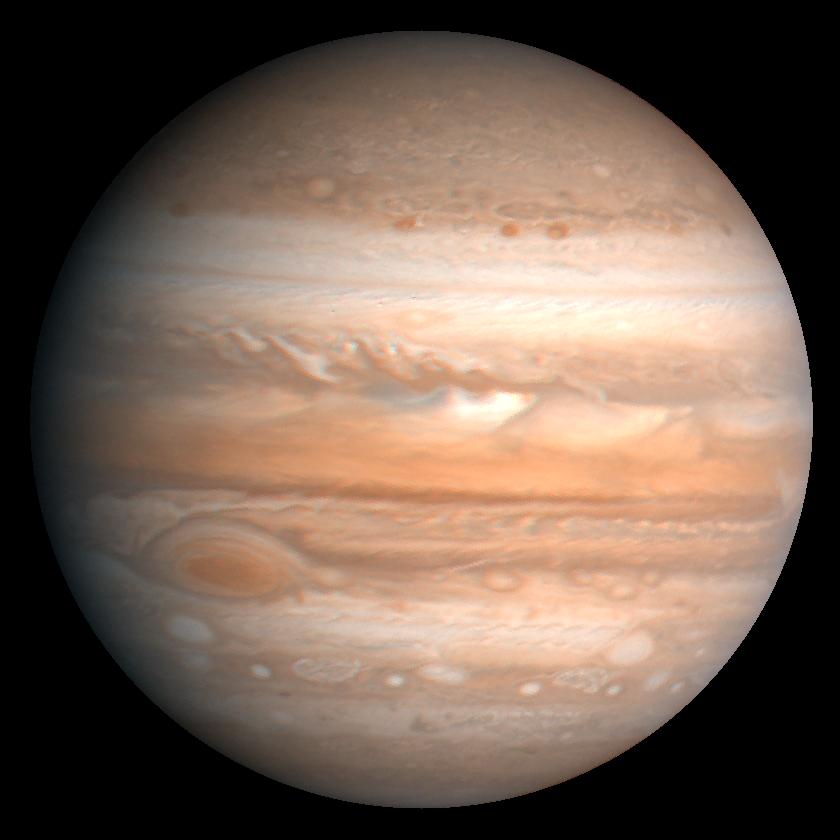
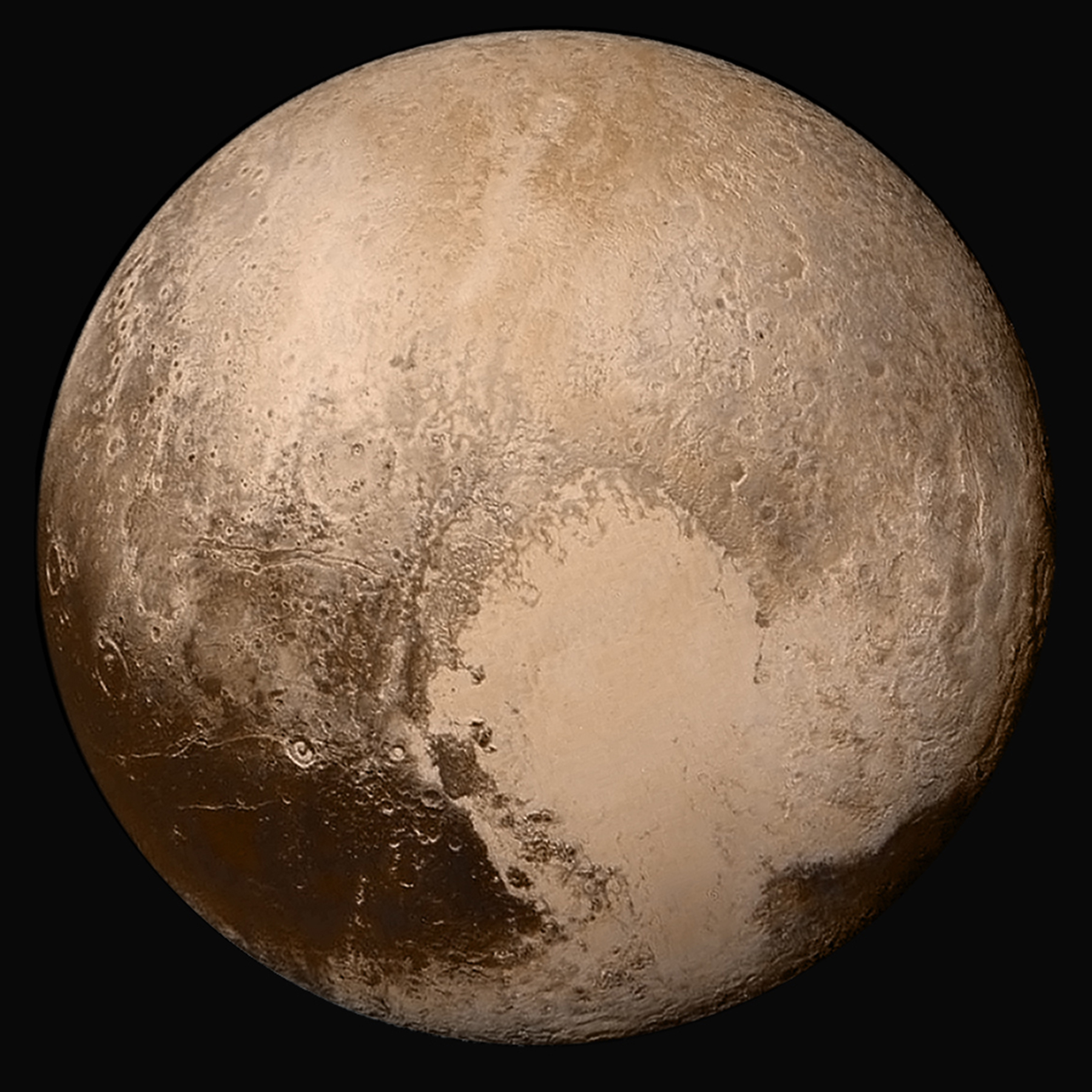
The Solar System is the planetary system of the Sun, to which the Earth belongs. Schematically, the Solar System is composed, in order of increasing distance from the Sun, of four internal telluric planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars), an asteroid belt made up of small rocky bodies, four giant gaseous outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune) and the Kuiper belt, itself made up of icy objects. The solar system is part of the galaxy called the Milky Way.
See more...